- Home
- About Us
- Conditions Treated
- Treatment Offered
- Testimonials
- Gallery
- News And Events
- Urology & Andrology
- Blogs
- Contact Us
Urinary incontinence could be defined as the inability to control the passage of urine from the bladder. Urinary incontinence is a common problem in both men and women. The complexity of this condition could range from occasional leakage of urine while coughing or sneezing to having constant and sudden urge to urinate.
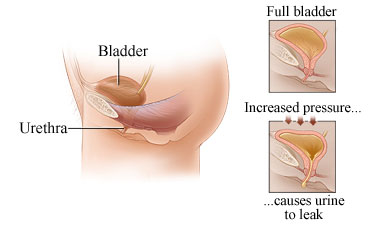
If urinary incontinence severely affects your daily activities, please consult your doctor immediately. Most often, certain simple lifestyle changes or medical treatment can relieve the discomfort or prevent urinary incontinence.
Causes of temporary urinary incontinence
Causes of persistent urinary incontinence
Tests & Diagnosis
Some of the common tests and procedures performed for diagnosis of urinary incontinence include:
Specialized testing
Additional tests often include:
Treatment for urinary incontinence
The treatment for urinary incontinence generally depends on the type of incontinence, the complexity of your problem and the specific cause.
Behavioral techniques
The doctor may recommend certain behavioral techniques and lifestyle changes for the treatment of certain types of urinary incontinence. This may include bladder training alone or in combination with other therapies, scheduled toilet trips or timed urination, fluid and diet management, weight loss or increased physical activity.
Physical therapy generally involves pelvic floor muscle exercises to strengthen your urinary sphincter and pelvic floor muscles and electrical stimulation. Often, various medications such as Anticholinergics, Topical estrogen. Imipramine and Duloxetine are used in combination with behavioral techniques.
Medical devices
Different kinds of medical devices are also available today to help treat incontinence including Urethral insert and Pessary.
Interventional therapies include bulking material injections, Botulinum toxin type A and Nerve stimulators that could help to control bladder function.
Surgery
If all the other conventional treatments have failed, surgical procedures are employed to treat urinary incontinence. This includes sling procedures. bladder neck suspension and artificial urinary sphincter.
Prevention
Here are some of the steps that you can follow to reduce your risk of incontinence:
Get in touch with us
Testimonials
About Dr. N. Anandan

Dr. N. Anandan is a senior consultant at Kauvery hospital and Apollo spectra hospitals in Chennai
Read MoreTreatments
Conditions Treated
Treatments Offered